Research
The Algorithms and Architectures for Reasoning and Intelligent Automation (ARIA) Lab advances interpretable, reliable, and intelligent AI systems through two tightly connected research directions. The first centers on probabilistic reasoning, neurosymbolic AI, and explainable AI, enabling transparent and structured decision making in domains such as computer vision and natural language processing. The second focuses on combinatorial and constrained optimization, emphasizing learning-based and neural approaches that power scalable reasoning and intelligent automation. Our work integrates structured domain knowledge with data-driven learning, producing methods that span graph-based inference, symbolic reasoning, and neural solvers for optimization, with applications in video understanding, activity recognition, human–computer interaction, and multimodal reasoning.
Research directions
- Inference in neurosymbolic models
- Neural network-based solvers for combinatorial optimization
- Video understanding and activity recognition
- Multi-label classification
Inference in neurosymbolic models
We build neural inference engines that plug into neurosymbolic models and answer hard queries like MPE, constrained MPE, and marginal MAP in (near) real time. The common thread is to treat the probabilistic model as the teacher, train neural approximators or neural network-based heuristics using self-supervision or distillation, and get near-optimal outputs in (near) real time.
Neural network-based approaches for constrained and unconstrained probabilistic inference
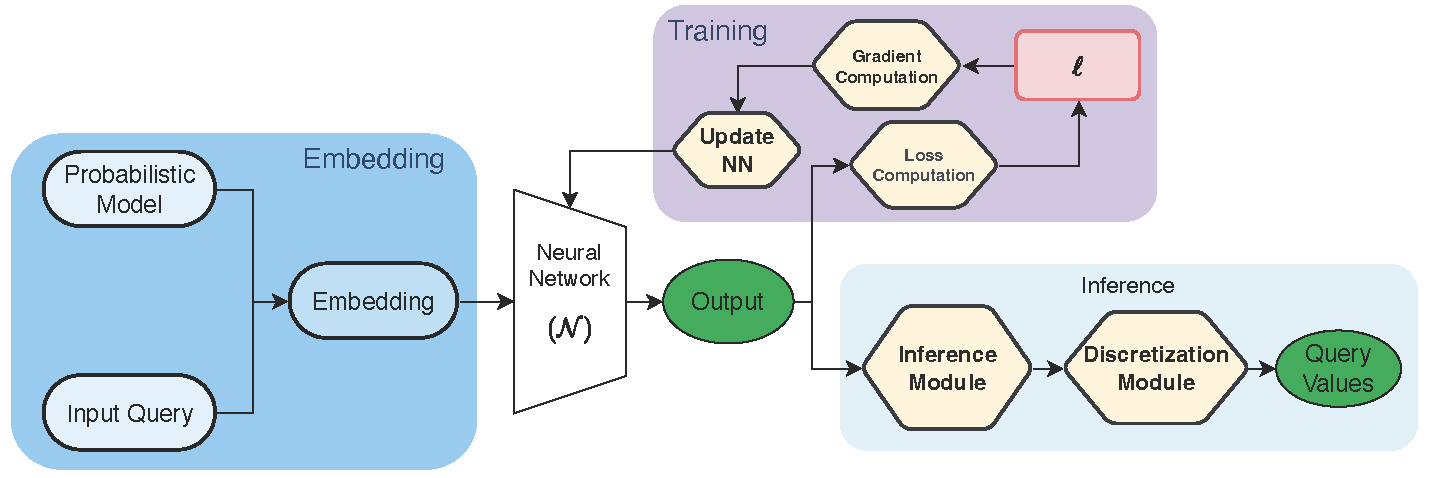
We design neural architectures that approximate probabilistic inference tasks directly: given a probabilistic model and evidence, the network outputs a high-quality solution to inference queries in one or a few forward passes, sometimes followed by test-time optimization.
- SINE: Scalable MPE Inference for Probabilistic Graphical Models using Advanced Neural Embeddings (AISTATS 2025)
- Learns rich structural and parameter-aware embeddings of graphical models, then uses advanced discretization schemes to get near-optimal MPE assignments.
- A Neural Network Approach for Efficiently Answering Most Probable Explanation Queries in Probabilistic Models (NeurIPS 2024 Spotlight; UAI TPM 2024 Best Paper)
- Distills all MPE queries for a given probabilistic model into a neural network and refines solutions via inference-time self-supervised optimization.
- Neural Network Approximators for Marginal MAP in Probabilistic Circuits (AAAI 2024 Oral)
- Uses neural approximators to solve marginal MAP in probabilistic circuits via a continuous multilinear relaxation and fast linear-time inference.
- Learning to Solve the Constrained Most Probable Explanation Task in Probabilistic Graphical Models (AISTATS 2024)
- Introduces a self-supervised framework for constrained MPE (CMPE) where feasibility and optimality are enforced through carefully designed loss functions.
Neural network-based heuristics for probabilistic inference
Here we learn heuristic policies that steer classical search-based inference algorithms, rather than directly predicting solutions.
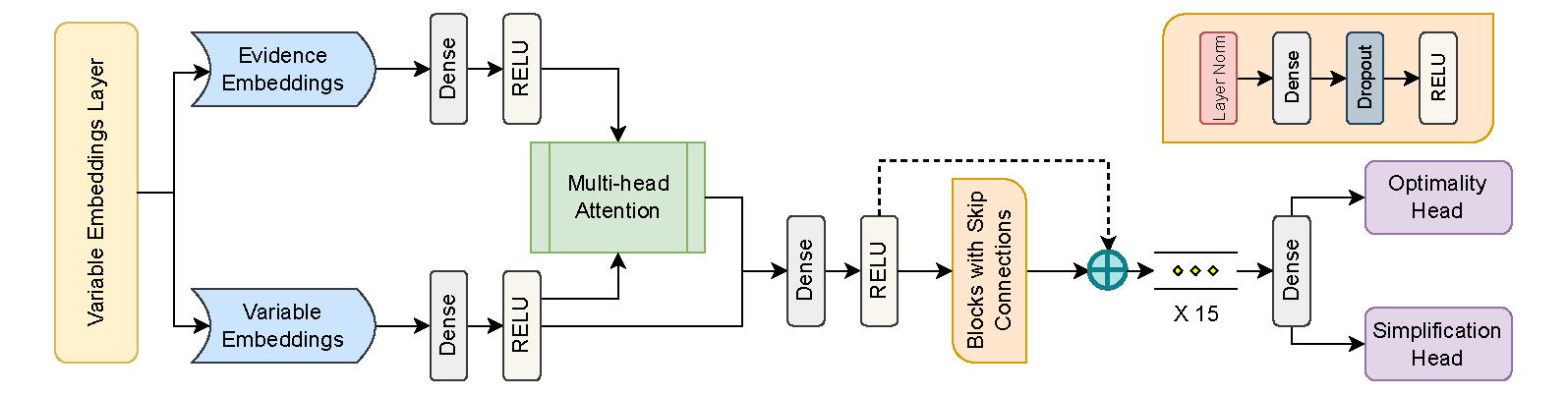
- Learning to Condition: A Neural Heuristic for Scalable MPE Inference (NeurIPS 2025)
- Introduces a scalable, data-driven framework for MPE inference that learns a neural conditioning policy from solver search traces, usable both as a conditioning strategy prior to exact inference and as a branching and node selection heuristic within branch-and-bound, significantly reducing the search space while maintaining or improving solution quality.
Optimization-based probabilistic inference schemes
We also look at optimization-based inference schemes in structured models, especially for multi-label prediction in images and videos.
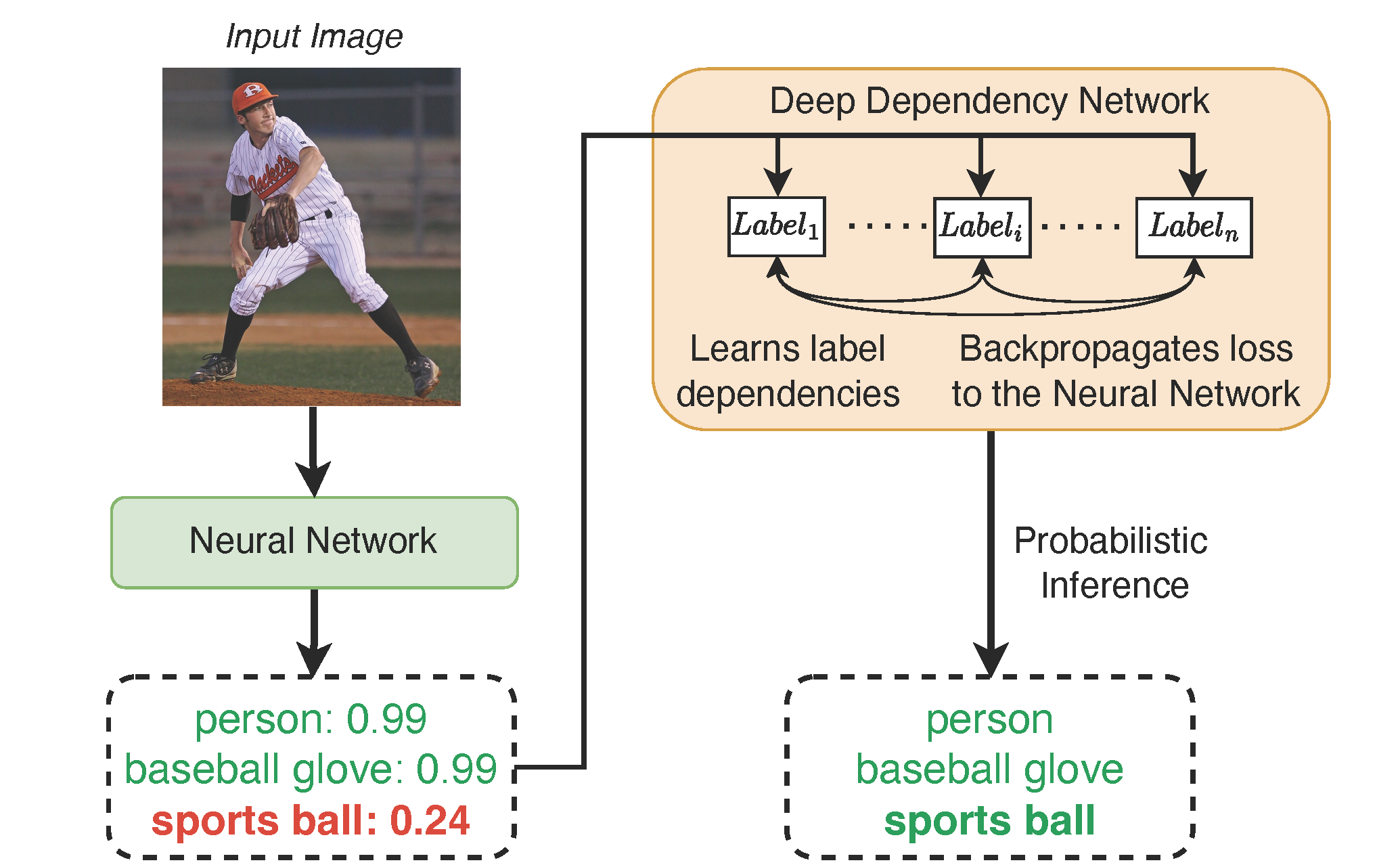
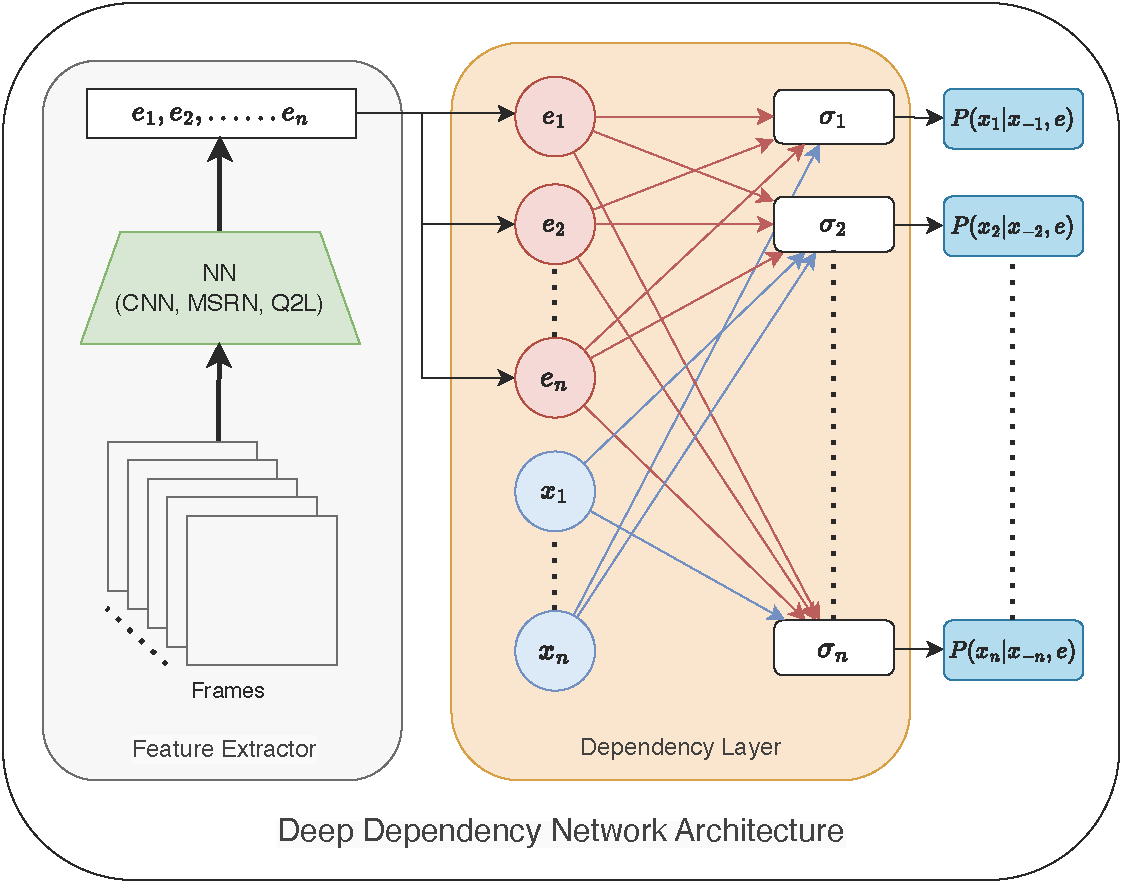
- Deep Dependency Networks and Advanced Inference Schemes for Multi-Label Classification (AISTATS 2024)
- Combines deep dependency networks with local search and integer linear programming–based inference to get strong multi-label predictions without sacrificing training simplicity.
Neural network-based solvers for combinatorial optimization
We design neural and reinforcement learning solvers for graph-structured combinatorial optimization problems that naturally arise in social and information networks.

- RELINK: Edge Activation for Closed Network Influence Maximization via Deep Reinforcement Learning (CIKM 2025)
- Formulates edge-level influence maximization in privacy-constrained networks as a Markov Decision Process and learns an edge-centric Q-learning policy that outperforms existing edge-based baselines.
Video understanding and activity recognition
We study procedural activities, error detection, and explanations in videos, often in egocentric or AR settings. The goal is to move beyond frame-level labels to structured, explainable video understanding models that support error analysis and human–AI collaboration.
- CaptainCook4D: a dataset for understanding errors in procedural activities (NeurIPS D&B Track2024; DMLR 2023)
- 94.5-hour egocentric 4D dataset of recipe execution with normal and errorful trials, annotated for error recognition, multi-step localization, and procedure learning.
- Explainable Activity Recognition in Videos Using Deep Learning and Tractable Probabilistic Models (ACM TiiS 2023)
- Feeds deep video features into dynamic cutset networks to get interpretable temporal models that can answer explanation queries while remaining competitive on recognition metrics.
- Predictive Task Guidance with Artificial Intelligence in Augmented Reality (IEEE VR 2024 Workshop / Poster)
- Explores AI-driven, predictive AR guidance for complex tasks, using structured models that anticipate user actions and provide proactive support.
Multi-label classification
We also work on classical multi-label learning methods that connect to our structured and probabilistic inference interests.
- Multi-Label Classifier based on Kernel Random Vector Functional Link Network (IJCNN 2020)
- Proposes a kernelized RVFL-based multi-label classifier with pseudo-inverse training and robust thresholding, showing strong performance on benchmark multi-label datasets.