Advanced Mpe Inference Schemes For Dependency Networks
Deep Dependency Networks (DDNs) combine dependency networks with deep neural architectures to tackle multi-label classification on images and videos.
They keep the easy training of dependency networks while adding strong inference via local search and integer linear programming (ILP), going beyond standard Gibbs sampling.
Model & Inference
We build a dependency network on top of deep encoders (CNNs / video backbones). For each label (X_i), the network learns a conditional distribution (p(X_i \mid \text{parents}(X_i), e_i)) using a sigmoid output layer fed by learned features (e_i).
- Training: straightforward maximum-likelihood-style training using the DDN loss (one conditional per label).
- Inference: we focus on computing the most probable explanation (MPE) configuration of labels given the image/video.
- Schemes supported:
- Gibbs sampling
- Local search–based methods
- Multi-linear integer programming (MILP)
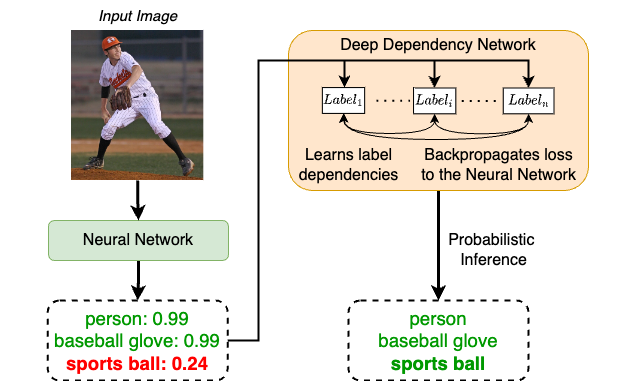
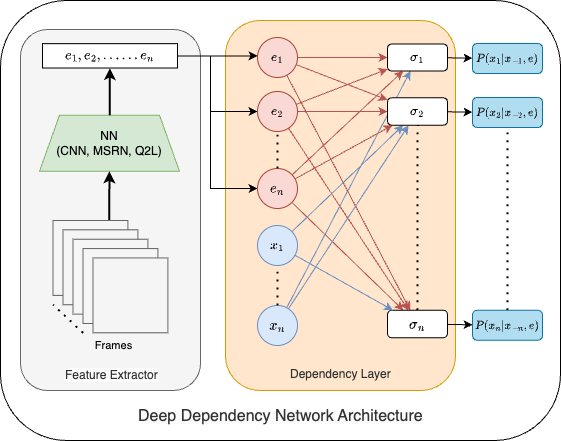
Annotation Comparison
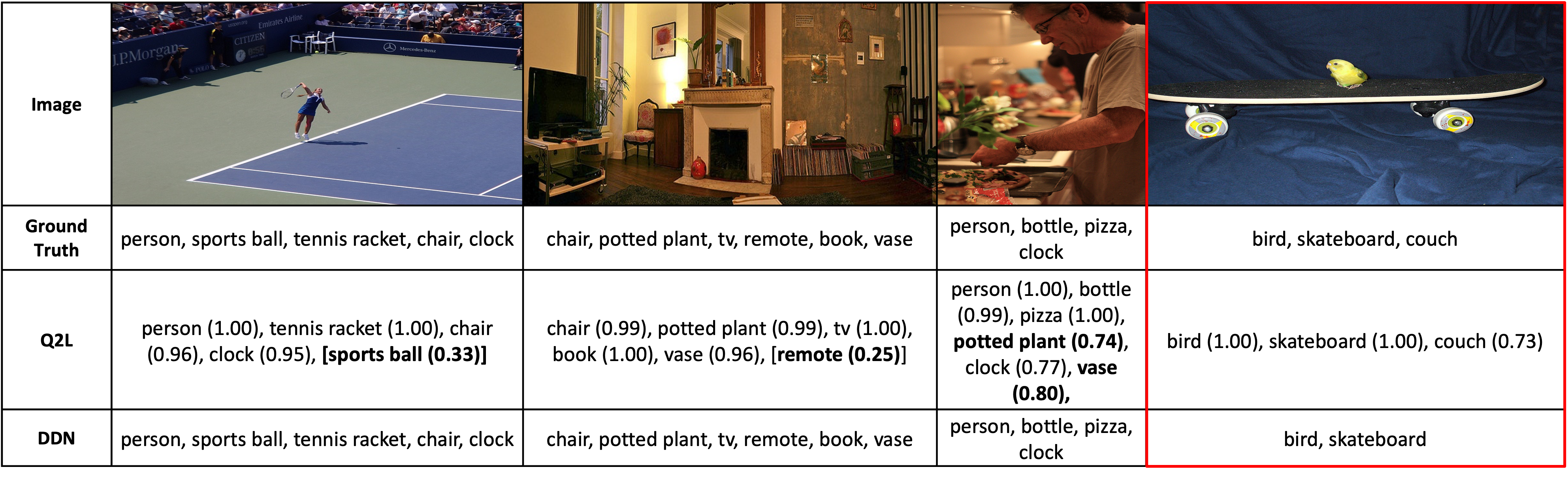

Datasets & Results
We evaluate on:
- Video: Charades, TACoS, Wetlab
- Image: MS-COCO, PASCAL VOC, NUS-WIDE
Across these benchmarks, our advanced DDN inference schemes outperform:
- (a) strong neural baselines without structured inference, and
- (b) neural + Markov network models equipped with advanced inference/learning.
Getting the Code
The official implementation includes:
- Joint training of DDNs across all datasets above.
- Implementations of Gibbs sampling, local search, and MILP-based inference.
- Environment files for each dataset and for the advanced inference schemes.
See the project README and MODEL_ZOO.md files in the code repository for:
- Exact environment setup (per dataset and for advanced inference),
- Pretrained models and baseline implementations,
- Scripts for training and running the different inference strategies.